There are three main reasons to get a battery: emergency backup power, financial savings and maximizing self-supply of solar. But even beyond these reasons to purchase storage for your home or business, there are plenty of benefits from energy storage for you individually, as well as for society as a whole. Here are a few of the benefits provided by energy storage, split based on the benefits for home and business owners and for the grid/society writ large.
Energy storage has four primary benefits we’ll cover: resiliency, cost savings, renewable integration, and additional grid benefits.
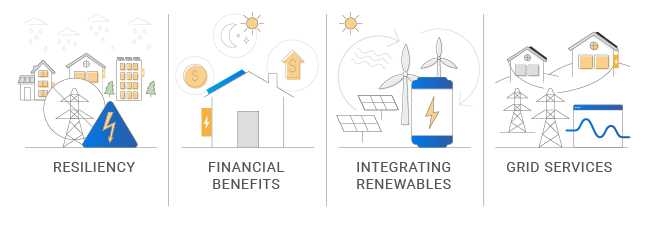
In the energy industry, resiliency is the ability to keep the electricity on even in the event of adverse conditions, such as major storm events or other types of utility outages. And that’s exactly what energy storage provides: emergency backup power. When you pair energy storage with a solar panel system, you can keep your lights on even in the event of a grid outage. These days, the primary reason that most home and business owners add energy storage is for the resiliency benefit.
Although backup power is the primary reason that people install energy storage today, storage systems can also provide financial benefits in some scenarios. The two main ways that storage can provide financial benefits is if you are on a time of use rate or if you have demand charges. In either of those instances, you can pull from your battery instead of from the grid at times when you’d be charged at a higher rate. Additionally, energy storage can help maximize the financial savings you get from solar if you don’t have access to one-to-one net metering by allowing you to consume more of the solar you produce on site.
One of the biggest benefits of energy storage is that it helps the grid to better integrate renewable energy. In that way, it’s an enabling technology for other clean energy technologies. Here’s how:
The main counterpoint against renewable energy technologies is the variability of their power production. Whereas the electric grid was built to accommodate fossil fuel-fired power plants that can turn on when called upon to meet demand, renewable energy resources produce when the sun is shining and the wind is blowing. As more and more renewable power facilities are built, there’s a need to better align their output with demand for electricity.
That’s where energy storage can come into play. When energy storage is paired with renewable resources, it can make renewable energy “dispatchable”, meaning it can be stored for use when it’s needed and called upon. In other words, energy storage lets wind and solar operate nearly the exact same way as existing power plants do, but without the emissions!
Energy storage does more for the grid than just allow for additional renewable energy. There are many different services that are necessary to keep our electrical system up and running and energy storage can provide most, if not all, of those services.
For instance, in the US, the electrical grid operates at a frequency of 60 hertz. A frequency deviation by more than a couple of tenths of a point (say 0.5 hertz) can cause cascading blackouts. Today, a number of different types of resources provide frequency regulation and support. Energy storage is another technology that can provide frequency support, decreasing the need for fossil fuel-powered resources on the grid.
And energy storage can play a much bigger role even than that: it can provide fast acting, quick response injections of energy on the grid as a contingency, it can provide reserves, and it can even provide black-start capability. All of which is to say that energy storage is a very flexible, useful resource that can provide loads of benefits to the grid.